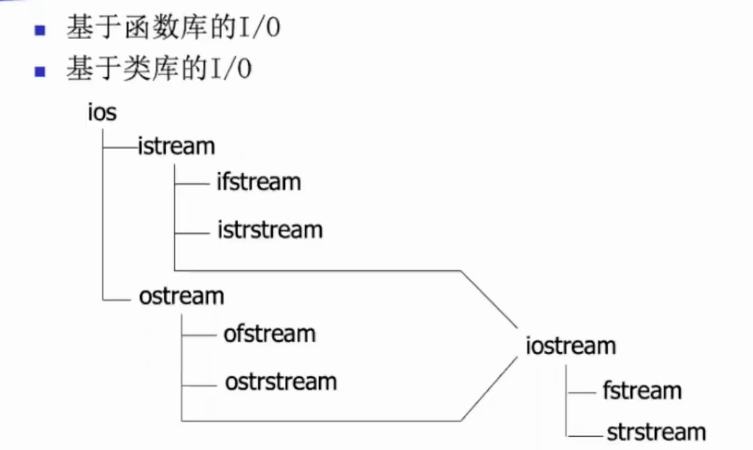
cout是带缓冲的,可以进行重定向cerr不带缓冲的,用来打印错误信息clog是带缓冲的
重定向 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ifstream in ("in. txt" ) ;streambuf * cinbuf = cin. rdbuf (); cin. rdbuf ( in. rdbuf ()); ofstream out (" out. txt " ) ;streambuf * coutbuf = cout. rdbuf (); cout. rdbuf ( out. rdbuf ()); string word; cin >> word; cout << word << " " ; cin. rdbuf ( cinbuf ); cout. rdbuf ( coutbuf ); cin >> word; cout << word;
I/O处理 对输出操作符<<进行重载,只能采用友元函数的形式进行,而不能将operator<<()申明为ostream类的成员函数。这是因为ostream是在C++标准中定义的类,不允许用户随便修改。 所以,要将类someClass的对象输出到标准输出对象,只能采用将operator<<()重载为全局函数,申明为someClass类的友元的形式进行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class CPoint2D { double x, y; public : friend ostream& operator << (ostream&, CPoint2D &); }; ostream& operator << (ostream& out, CPoint2D& a){ out << a.x << "," << a.y << endl; return out; } CPoint2D a; cout << a; --------------------------------------------------------------------------- class CPoint3D : public CPoint2D{ double z; } CPoint3D b; cout << b; class CPoint3D : public CPoint2D{ double z; friend ostream& operator << (ostream &, CPoint3D &); } ostream& operator << (ostream& out, CPoint3D & b){ out << b.x << "," << b.y <<"," << b.z << endl; return out; }
虚化:虚化非成员函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class CPoint2D { double x, y; public : … virtual void display (ostream& out) { out << x << ‘,’ << y << endl; }}; ostream& operator << (ostream& out, CPoint2D &a) { a.display (out); return out; } class CPoint3D : public CPoint2D{ double z; public : … void display (ostream& out) { CPoint2D::display (); out << ‘,’<< z << endl; }};
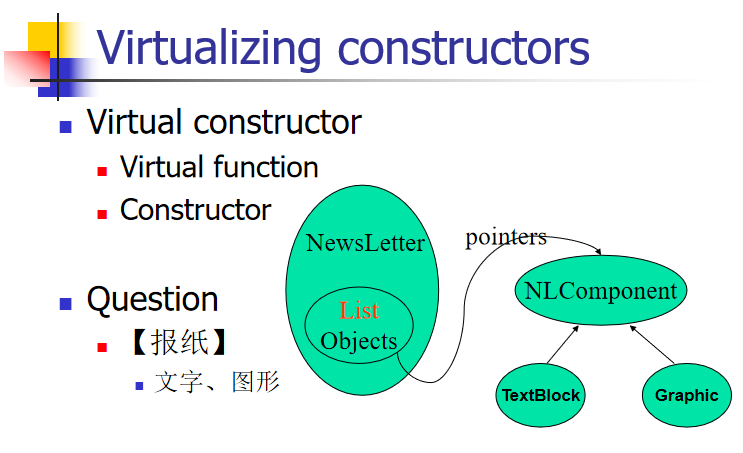
虚拟化构造器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class NLComponent {…};class TextBlock :public NLComponent {…};class Graphic :public NLComponent {…};class NewsLetter { public : NewsLetter (istream& str){ while (str) components.push_back (readComponent (str)); } static NLComponent * readComponent (istream& str) NewsLetter (const NewsLetter& rhs){ for (list<NLComponent *>::iterator it=rhs.component.begin ();it != rhs.component.end (); ++it ) component.push_back (); } private : list<NLComponent *> components; } virtual NLComponent *clone () const 0 ; virtual TextBlock *clone () const return new TextBlock (*this ); } virtual Graphic *clone () const return new Graphic (*this ); } NewsLetter::NewsLetter ( const NewsLetter& rhs){ for ( list<NLComponent *>::iterator it=rhs.component.begin (); it != rhs.component.end (); ++it ) component.push_back ((*it)->clone ()); } class BST {};class BalancedBST : public BST {};void printBSTArray (ostream& s, const BST array[], int numElements) for (int i=0 ; i < numElements; i++) s << array[i]; } BalancedBST bBSTArray[10 ]; printBSTArray (cout, bBSTArray, 10 );
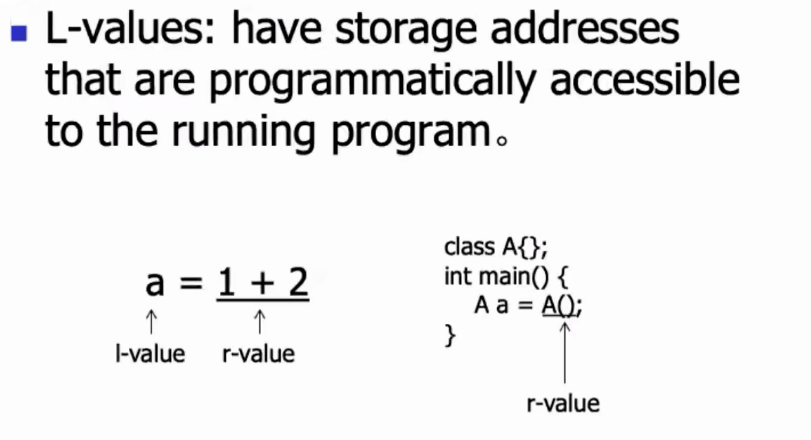
C11新特性 右值引用 R-value Reference
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class MyArray { int size; int *arr; public : MyArray ():size (0 ),arr (NULL ){} MyArray (int sz): size (sz),arr (new int [sz]) { } MyArray (const MyArray &other): size (other.size), arr (new int [other.size]) { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { arr[i] = other.arr[i]; } } MyArray (MyArray &&other): size (other.size), arr (other.arr) { other.arr = NULL ; } ~ MyArray () { delete [] arr; } } MyArray change_aw (const MyArray &other) MyArray aw (other.get_size()) ; return aw; } int main () MyArray myArr (5 ) ; MyArray myArr2 = change_aw (myArr); MyArray &&myArr2 = change_aw (myArr); MyArray myArr2 = change_aw (myArr); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class MyArray {public : MyArray &operator =(const MyArray &other) { if (this == &other) return *this ; if (arr) { delete [] arr; arr = NULL ; } size = other.size; memcpy (arr, other.arr, size * sizeof (int )); return *this ; } MyArray &operator =(ArrayWrapper &&other) { size = other.size; arr = other.arr; other.arr = NULL ; return *this ; } } int main () MyArray myArr; myArr = MyArr (5 ); }
拷贝构造、拷贝赋值、移动构造、移动赋值、析构函数
外部模板 Extern Templates 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 template <typename T> void myfunc (T t) {}#include "myfunc.h" int foo (int a) myfunc (1 ); return 1 ; } #include "myfunc.h" extern template void myfunc <int >(int ); int main () myfunc (1 ); }
常量表达式 Constant Expression
提供了更一般的常量表达式
允许常量表达式使用用户自定义类型
提供一种方法来确保在编译时完成初始化
必须在编译的时候可以确定常量表达式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 enum Flags { GOOD=0 , FAIL=1 , BAD=2 , EOF=3 };constexpr int operator | (Flags f1, Flags f2) { return Flags (int (f1)|int (f2)); } void f (Flags x) switch (x) { case BAD: break ; case EOF: break ; case BAD|EOF: break ; default : break ; } } void f (Flags x) switch (x) { case bad_c () : /* ... */break; case eof_c () : /* ... */ break; case be_c () : /* ... */ break; default : break ; } } constexpr int bad_c () constexpr int eof_c () constexpr int be_c ()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 struct Point { int x,y; constexpr Point (int xx, int yy) : x(xx), y(yy) { }; int main () constexpr Point origo (0 ,0 ) constexpr int z = origo.x; constexpr Point a[] = {Point (0 ,0 ), Point (1 ,1 ), Point (2 ,2 ) }; constexpr int x = a[1 ].x; }
所有评估都可以在编译时完成,所有对象都可以看做一组值。 因此,提高了运行时间效率。
编译时确定的
Lambda 表达式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 bool cmpInt (int a, int b) return a < b;}class CmpInt { bool operator () (const int a, const int b) const return a < b; } }; int main () std::vector<int > items { 4 , 3 , 1 , 2 }; std::sort (items.begin (), items.end (), cmpInt); std::sort (items.begin (), items.end (), CmpInt ()); std::sort (items.begin (), items.end (), [](int a, int b) { return a < b; } ); return 0 ; } template <class RandomAccessIterator , class Compare > void sort (RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp) if ( comp (*it1, *it2) ) } std::function<bool (int , int ) > f1 (cmpInt) ;std::function<bool (int , int ) > f2 (CmpInt) ;std::function<bool (int , int ) > f3 ([](int a, int b) { return a < b;} ) ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 vector<string> str_filter (vector<string> &vec, function<bool (string &)> matched) { vector<string> result; for (string tmp : vec) { if (matched (tmp)) result.push_back (tmp); } return result; } int main () vector<string> vec = {"www.baidu.com" , "www.kernel.org" , "www.google.com" }; string pattern = ".com" ; vector<string> filterd = str_filter (vec, [&](string &str) { if (str.find (pattern) != string::npos) return true ; return false ; }); }
符号 含义
[]
Capture nothing
[&]
Capture any referenced variable by reference
[=]
Capture any referenced variable by making a copy 以值拷贝的方式传入,不会产生副作用
[=, &foo]
Capture any referenced variable by making a copy, but capture variable foo by reference
[bar]
Capture bar by making a copy; don’t copy anything else
Delegating Constructor 委托构造函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #define MAX 256 class X { int a; void validate (int x) if (0 <x && x<=MAX) a=x; else throw bad_X (x); } public : X (int x) { validate (x); } X () { validate (42 ); } }; class X { int a; public : X (int x) { if (0 <x && x<=max) a=x; else throw bad_X (x); } X () :X (42 ) { } }; X (int x = 42 ) ?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 vector<int > vec; vec.push_back (1 ); vector<int > vec = {1 , 2 , 3 }; template class vector <T> { vector (initializer_list<T> list) { for (auto it = list.begin (); it != list.end (); ++it) push_back (*it); } }; int arr[] = {1 , 2 , 3 }; vector<int > vec = {1 , 2 , 3 }; A a= {1 , 2 , 3 }; class A { int x, y, z; A (initializer_list<int > list) { auto it = list.begin (); x = *it++; y = *it++; z = *it; } }; int arr[] = {1 , 2 , 3 };vector<int > vec = {1 , 2 , 3 }; A a = {1 , 2 , 3 };
nullptr 空指针 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void f (int ) void f (char *) f (0 ); f (nullptr ); f (NULL );